
A sequential approach to fabricate 3D/2D tin perovskite solar cells
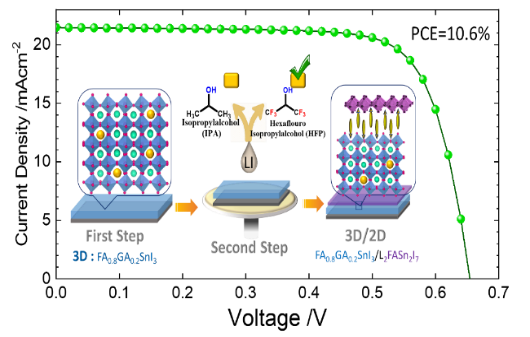
To solve the toxic issue for new-generation photovoltaic applications, tin-based perovskite solar cells are a promising alternative to their lead counterparts, but they suffer from poor stability because of their tendency of tin oxidation. Herein we developed a sequential method of solution processing to fabricate hybrid 3D/2D tin-based perovskite solar cells with great device performance and stability. The FA/GA co-cationic 3D film (E1G20) was prepared according to a one-step procedure. Using HFP as a solvent in the second step of deposition would induce a strong interaction between BAC and HFP to slow the reaction of BAC with the E1G20 film and to produce a thin layer of a 2D (n = 1) phase or a quasi-2D phase. Among all eight BAC under investigation, anilinium (AN) was found to form an ultra-thin 2D layer on the surface and between the grain boundaries to protect the tin perovskite layer from moisture penetration so as to enhance the device performance to attain PCE 10.6%. The unencapsulated AN device is stable under ambient air and a self-healing effect was found for the encapsulated AN cell under continuous one-sun illumination and thermal stress between 20 and 50 C for 10 cycles. The present work thus provides a new route for the development of lead-free perovskite solar cells using a sequential procedure for future commercialization.
Efat Jokar, Po-Yuan Cheng, Chia-Yi Lin, Sudhakar Narra, Saeed Shahbazi and Eric Wei-Guang Diau,* “Enhanced Performance and Stability of 3D/2D Tin Perovskite Solar Cells Fabricated with a Sequential Solution Deposition”, ACS Energy Lett. 6, 485 (2021).
Self-Assembled Monolayer (SAM) Applied for Tin Perovskite Solar Cells via a Two-Step Fabrication
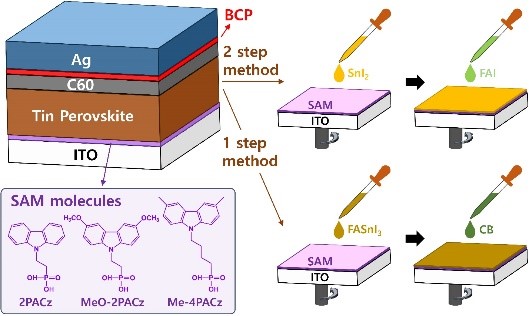
High-performance tin perovskite solar cells (PSC) have been extensively explored using PEDOT:PSS as a hole-transport material (HTM) layer according to a one-step fabrication method. This work is the first report on HTM-free tin-based PSC using the concept of self-assembled monolayer (SAM) to modify the ITO surface using a two-step deposition method. Herein we developed a preheating procedure to effectively reduce the amounts of hydroxyl groups and oxygen vacancies on the ITO surface for a uniform SAM to form. We found that the ITO substrate preheated at 400 °C gives the best device performance for efficiency of power conversion attaining 6.5% with excellent enduring stability in a glovebox for 1900 h without encapsulation. Studies on electrochemical impedance spectra (EIS), time-correlated single photon counting (TCSPC) and femtosecond transient absorption spectra (TAS) were carried out to understand the interfacial charge recombination and hole-extraction kinetics in relation to the observed device performance. The present work thus provides a new direction for the development of HTM-free lead-free perovskite solar cells for their future up-scale production.
Donghoon Song, Sudhakar Narra, Meng-Yu Li, Jian-Sing Lin and Eric Wei-Guang Diau*, “Interfacial Engineering with a Hole-Selective Self-Assembled Monolayer for Tin Perovskite Solar Cells via a Two-Step Fabrication”,ACS Energy Lett. 6, 4179 (2021).